THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO WELDING
FUME EXTRACTION SYSTEMS:
HOW (AND WHY) TO KEEP YOUR FACILITY AIR CLEAN AND SAFE
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO WELDING FUME EXTRACTION SYSTEMS:
HOW (AND WHY) TO KEEP YOUR FACILITY AIR CLEAN AND SAFE
The Complete Guide to Weld Fume Extraction represents current best practices and recommended strategies for weld fume removal in industrial facilities. This essential guide covers all of the basics for designing a weld fume mitigation strategy for metalworking facilities, fabrication shops and large manufacturers. Includes:
- Weld fume characteristics and health risks
- OSHA Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for weld fumes along with ACGIH and NIOSH recommended limits
- General principles of weld fume removal, including exhaust ventilation, source capture and ambient air filtration
- Considerations in dust collection system design, including capture method, hood design, dust collector types, air velocity, filter selection, and methods for collecting fugitive weld fume not captured by the primary system
- Progressive filtration strategies for control of submicron weld fume particulate
- Dust collector operation and maintenance

THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO
WELDING FUME EXTRACTION SYSTEMS:
HOW (AND WHY) TO KEEP YOUR FACILITY AIR CLEAN AND SAFE
WELD FUME EXTRACTION: COMPLETE GUIDELINES ONLINE
Learn how to protect welders from dangerous weld fumes and keep your facility in compliance with OSHA or local regulations for weld fume safety.
Who is this guide for?
The weld fume extraction guidelines provide an in-depth overview of the fundamentals of weld fume safety, exposure limits and fume capture options for both robotic welding and manual welding. It is aimed at decision-makers, operational managers, safety and compliance directors, and others who need a better understanding of weld fume fundamentals to make effective mitigation decisions. This is a general overview of weld fume removal strategies for metalworking and fabricating shops, large manufacturers using robotic welding, weld schools, and other environments where manual or robotic welding are used.
This guide is not designed to replace the need for an engineering consultation. Consult with a qualified air filtration engineering partner when making final system design decisions.

EXPLORE THE CHAPTERS
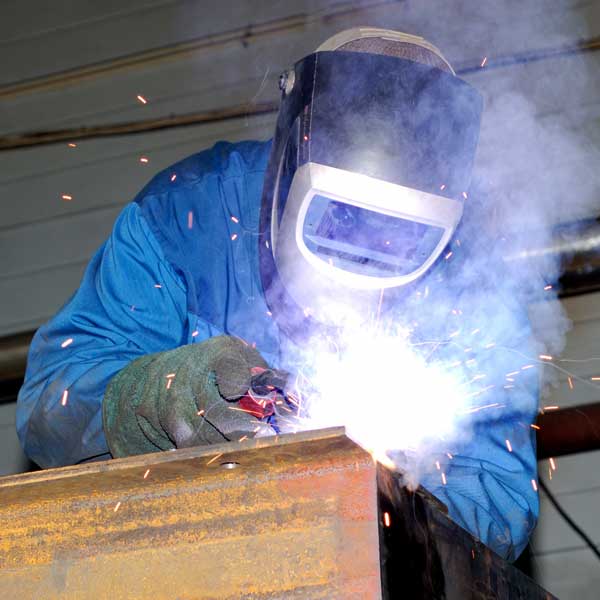
Weld fumes create hazards for welders and others who are exposed to fumes that can propagate throughout the space. Understanding the composition of weld fumes and their health and safety risks is the first step to designing a weld fume removal strategy.
In designing a weld fume mitigation strategy, it is important to understand the goals you want to set in terms of weld fume exposure and overall indoor air quality (IAQ). This starts with knowing the regulatory limits for exposure to weld fume.
Weld fume controls must be put into place to prevent welders from breathing in harmful fumes and to prevent fumes from propagating through the facility.
Source capture is considered to be a best practice for weld fume collection and is preferred wherever possible. Source capture systems collect contaminants close to the source where they are produced, keeping them out of the breathing zone for manual welders and preventing the propagation of weld fumes throughout the facility.
Ambient air filtration may be used as a stand-alone weld fume solution where source capture is not possible or as part of a hybrid solution that includes both source capture and general/ambient filtration.
Filter selection is an important component of both source capture and ambient air filtration system design. Filters for weld fumes must be capable of capturing the very small, sub-micron particulate created by thermal processes such as welding.
An air filtration system must be properly installed and maintained to ensure that expected results are achieved.