DUST COLLECTOR CARTRIDGE FILTERS
High-Quality Replacement Filters for Industrial Dust Collectors
Cartridge air filters are the heart of your dust collection system. Protect your people and ensure compliance with indoor air quality (IAQ) regulations with high-quality dust collector cartridge filters from RoboVent. We manufacture our own cartridge filters to exacting standards to ensure longevity and performance. Let us help you find the right type of filter cartridge for your RoboVent dust collector and applications. Need replacement cartridge filters for Camfil, Donaldson, or other dust collection systems? No problem—we make OEM-quality replacement filters for most makes and models of cartridge dust collectors.

WE ARE THE CARTRIDGE AIR FILTER EXPERTS
Pleated cartridge filters for industrial dust collection come in a variety of media types, styles and options. Which dust collector filter is right for your application? Our Dust Collector Cartridge Filters Buyer’s Guide has all the details! Read the online guide to industrial cartridge filters and download our quick-reference cheat sheet to find the perfect filter for your dust collection application. Or talk to one of our filter specialists to get expert help in filter selection.
PLEATLOCK™ AND ENDUREX® RMO: OUR BESTSELLING PLEATED CARTRIDGE FILTERS
PleatLock and Endurex RMO are our top cartridge air filter brands for RoboVent dust collectors, including RoboVent Senturion® and RoboVent Spire®. Which dust collector filter is right for you?
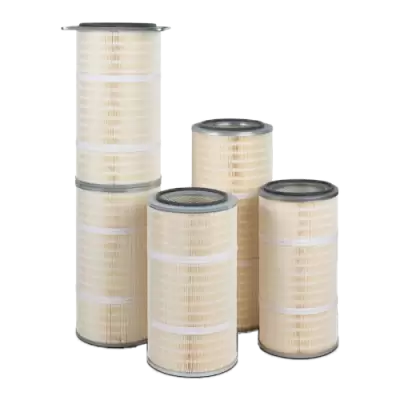

PleatLock
A high-performance cartridge air filter with an innovative pleat design that packs in 35% more filter media within the cartridge to extend filter life.
- More pleats per inch for a more compact, high-performing filter and an overall smaller dust collection system.
- Excellent filtration efficiency and performance.
- Cellulose polyester blends in MERV 11 or MERV 15.

Endurex RMO
An economical and versatile pleated cartridge air filter suitable for a range of applications, including fumes, smoke, dust and other dry particulate.
- Mini-pleat design with wider pleat spacing.
- RMO support to keep optimal separation between pleats and enhance airflow.
- Available in MERV 11, nanofiber MERV 15, and PTFE MERV 16.
AFTERMARKET REPLACEMENT FILTERS: FOR ALL YOUR DUST COLLECTION NEEDS
RoboVent manufactures high-quality replacement cartridge filters for most makes and models of industrial dust collectors. Order replacement dust collector cartridge filters for Camfil (Farr), Donaldson (Torit), Parker (Clarcor) and many other cartridge dust collector brands. Plus, replacement filters for baghouse dust collectors, pulse filters, HEPA filters, air cleaners and purifiers and dust, fume and mist collectors.
DUST COLLECTOR CARTRIDGE FILTER FAQS
Filtration Basics
Filtration Basics
What Is the MERV Rating System for Air Filters?
The MERV rating, which stands for Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value, is a standardized scale used to measure the effectiveness of air filters in capturing particles of specific sizes. The MERV rating system was developed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE). ASHRAE has developed filter efficiency and testing standards that are used for all types of air filters, including HVAC filters and filters used in industrial air filtration and ventilation. For cartridge filters in dust collectors, the MERV rating indicates how efficiently the filter captures airborne particles. MERV ratings range from 1 (least efficient) to 20 (most efficient). (Note: MERV ratings above 16 are equivalent to HEPA filtration; the highest rating typically used for industrial air filtration is MERV 16.) The higher the MERV rating, the finer the particles the filter can capture. Manufacturers must have their cartridge filters tested by a third-party laboratory using ASHRAE-approved testing methods to use the MERV rating system.
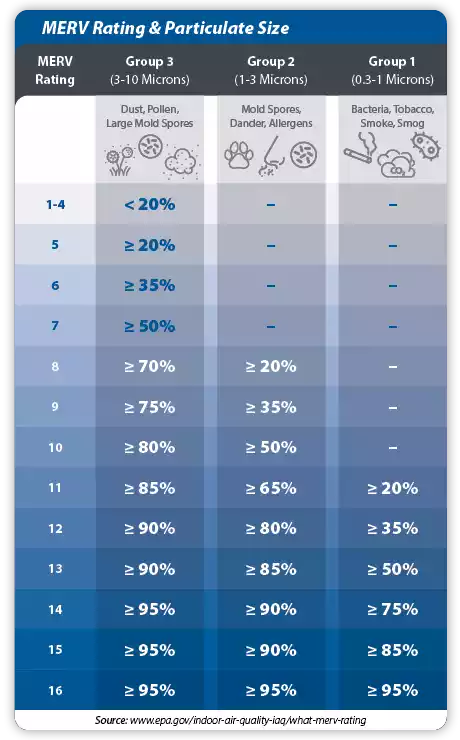
What Is ASHRAE 52.2?
ASHRAE Standard 52.2, officially titled “Method of Testing General Ventilation Air-Cleaning Devices for Removal Efficiency by Particle Size,” is a widely recognized standard developed by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE). It provides a standardized methodology for evaluating and determining the efficiency of air filters in removing particulate matter of specific sizes in general ventilation settings. ASHRAE 52.2 is critical in helping manufacturers, HVAC professionals, and end-users compare and select appropriate filters, ensuring that they perform adequately in mitigating particular airborne contaminants, thereby safeguarding indoor air quality (IAQ). For industrial dust collector filters, including baghouse and cartridge filters, ASHRAE 52.2 has been supplemented and updated by ASHRAE 199, which is specific to pulse-cleaned dust collection systems. Key aspects of ASHRAE 52.2 include:
- MERV Ratings: The standard introduces the Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV) rating system, assigning filters a rating from 1 to 20 based on their capability to remove airborne particles in specific size ranges. (Note: 17 and above are equivalent to HEPA and rarely used.) A higher MERV rating signifies better filtration performance.
- Particle Size Ranges: It evaluates filter efficiency across multiple particle size ranges, specifically focusing on particles between 0.3 and 10 microns, to determine how well a filter can remove different types of particulates.
- Testing Methodology: The standard outlines a specific procedure for testing filters, a means of measuring particle concentration, and a system for analyzing the data to calculate the filter’s performance.
What is ASHRAE 199?
ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 199 ("Method of Testing the Performance of Industrial Pulse Cleaned Dust Collectors") is a testing standard developed by ASHRAE specifically for evaluating the performance of industrial dust collection and fume extraction equipment. It provides a standardized and consistent method for measuring the performance of cartridge, baghouse or envelope-style industrial dust collectors, supplementing the general testing and rating requirements provided in ASHRAE 52.2. It applies specifically to dust collectors that use a filter pulsing mechanism to discharge dust from the filter surface while the collector remains online. This standard includes:
- Emissions Measurement: Determines the number of particulates (dust) escaping the system.
- Pressure Drop Measurement: Evaluates the resistance to airflow within the dust collector.
- Compressed Air Usage: Assesses how different systems utilize compressed air for pulse-cleaning of the filters.
What Is ASHRAE Standard 62.1?
ASHRAE Standard 62.1, titled “Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality,” addresses criteria for achieving and maintaining acceptable indoor air quality (IAQ) in commercial or institutional buildings, including industrial environments. The standard provides guidelines regarding air cleaning and filtration to mitigate particulate and gaseous contaminants. While ASHRAE 62.1 is primarily concerned with HVAC and ventilation systems rather than industrial dust collection, there are principles that can apply more broadly to industrial air filtration. This includes the specification of minimum efficiencies for air filters (using MERV ratings), which can guide the selection of cartridge filters in dust collection systems within industrial settings. ASHRAE standards should be considered along with other requirements, such as OSHA Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for industrial air pollutants.
What Is ASHRAE 129?
ASHRAE 129-1997 (RA 2002), titled “Measuring Air Change Rates in Buildings,” provides methods for measuring air change rates in buildings and building spaces, which are essential for understanding the ventilation effectiveness of these environments. ASHRAE 129 focuses on defining repeatable methods of measuring air change rates, applicable in various settings, such as commercial, residential, and industrial buildings. The methods encompassed in the standard include tracer gas dilution methods, continuous-injection tracer gas method, occupied building or occupied space method, concentration decay method, and constant concentration method. While this standard does not directly reference cartridge air filters, understanding the required air change rate to meet air quality targets impacts dust collection and air filtration system design, including filter selection and dust collector sizing.
What Is a HEPA After-Filter, and When Do I Need One?
A HEPA after-filter is a high-efficiency filtration unit designed to capture extremely fine particles that might not be adequately trapped by standard cartridge air filters in a dust collection system. HEPA stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air, and a filter must capture 99.97% of particles 0.3 microns in size to qualify as HEPA. In a dust collection system, an after-filter is typically positioned after the primary cartridge filter, serving as a secondary filtration stage. If you’re dealing with particularly fine or harmful dust or if you have stringent air quality requirements, a HEPA after-filter can be a valuable addition to your dust collection system. You might consider using a HEPA after-filter in situations where:
- The process generates very fine particles that pose a health risk or can contaminate products.
- Regulatory or industry standards require extremely high air quality.
- The collected dust contains hazardous materials, allergens, or carcinogens.
- You aim to recirculate filtered air back into the facility, necessitating cleaner air to improve indoor air quality.
What Is an Activated Carbon After-Filter, and When Do I Need One?
An activated carbon after-filter in a dust collection system is utilized primarily for odor control and removal of gaseous pollutants from the air. Activated carbon has a highly porous surface and excels at adsorbing a wide variety of odorous substances and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). After the dust collector’s primary filtration unit (e.g., the cartridge filter) captures particulate matter, the activated carbon after-filter engages to trap and remove unwanted odors and gases, ensuring that the air emitted from the system is not only free of particles but also smells clean and is void of gaseous contaminants. This additional step is particularly valuable in industries such as recycling or chemical manufacturing where odorous compounds or VOCs are prevalent, ensuring improved indoor air quality (IAQ) and compliance with air quality standards and regulations.
What Is Molecular Air Filtration?
Molecular air filtration refers to the process of removing gaseous, odorous, or otherwise molecular contaminants from the air using media that adsorb, absorb, or react/bond with the molecules. Rather than capturing particles, like typical air filters, molecular filtration targets airborne molecules through chemical or physical bonding (e.g., adsorption or absorption), often utilizing materials like activated carbon or specialized chemical media. This type of filtration is particularly useful in environments where clean, odor-free air is paramount or where harmful gaseous contaminants need to be controlled, such as laboratories or industrial settings, ensuring a safe and compliant atmosphere by addressing both particulate and molecular pollutants.
About Dust Collector Cartridge Filters
About Dust Collector Cartridge Filters
What Are Dust Collector Cartridge Filters?
Dust collector cartridge filters are cylindrical filtration devices used in cartridge dust collection systems to capture and remove fine airborne particles from the air. They are made from pleated filter media, which increases the surface area for capturing dust. The pleated cartridge design allows for better filtration efficiency and airflow than traditional bag filters. These filters are commonly used in industries such as metalworking, welding, woodworking, paper and cardboard processing, and powder and bulk applications such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, where the removal of fine dust particles is crucial for maintaining air quality and safety standards.
What Are the Advantages of Cartridge Air Filters for Dust Collection?
Dust collector cartridge filters offer several advantages. First, their pleated design provides a larger filtration surface area compared to traditional bag filters, leading to greater dust-holding capacity and extended filter life. This means that more filtration capacity is packed into a smaller space, which is why cartridge dust collectors are physically smaller and more energy efficient than other types of dust collectors, such as baghouse, with the same CFM and filtration capacity. Additionally, cartridge filters are often easier to install and replace than bag filters, reducing maintenance time. Moreover, many cartridge filters come with advanced media options that can capture very fine particles, enhancing air quality and ensuring compliance with stringent industry regulations. Cartridge dust collector filters are highly versatile and come in a range of media types for different dust collection applications.
What Is the MERV Rating for an Industrial Dust Collector Cartridge Filter?
For industrial applications, cartridge filters often have a MERV rating between 10 and 16, with higher-end filters used in environments where capturing very fine particulates is critical. Over time, cartridge filters will build a dust cake on the surface that will provide filtration approaching MERV 16. However, to ensure proper performance across the entire life of the cartridge filter, it is essential to select a cartridge filter with an appropriate MERV rating for the specific dust collection needs of the facility.
- Cartridge filters with a MERV rating of 10-12 can be used for larger particulate and less toxic applications such as non-toxic bulk and powder applications, manual metal grinding or cutting, woodworking, etc.
- A cartridge dust collector filter with a MERV rating of 15 or higher is recommended for welding and other processes with thermal fumes or fine powders.
- A HEPA or ULPA after-filter may be required for highly toxic materials or very fine submicron particulates.
What Are Cartridge Air Filters Used For?
Cartridge dust collector filters are designed to capture and remove airborne dust and particulate matter from industrial environments. They are used in a cartridge dust collection system. These filters are essential in places where operations produce a significant amount of dust, such as in woodworking shops, metal fabrication facilities, and various manufacturing processes. The primary function is to maintain indoor air quality, protect machinery from excessive dust buildup, and ensure a safe environment for workers by preventing the inhalation of harmful particulates. By keeping the air clean and compliant with safety standards and OSHA PELs, cartridge filters play a vital role in many industrial settings. Industries that use cartridge air filters for dust collection include:
- Metalworking, machining and general fabrication (including laser and plasma cutting, grinding, surface finishing, etc.)
- Plastic and rubber manufacturing
- Paper and cardboard manufacturing, recycling and bookbinding
- Welding
- Food processing
- Woodworking
- Pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals
- Chemical manufacturing (powder & bulk applications)
- Electronics manufacturing
- Battery manufacturing
- Mining and mineral processing
- Recycling
See more Industries and Applications.
What Is the Difference Between a Cartridge Air Filter and a Baghouse Filter?
Cartridge air filters and baghouse filters are both used in dust collection and air filtration systems, but they have distinct designs, characteristics, and best-use scenarios. Cartridge air filters are typically cylindrical in shape and constructed with pleated filter media, increasing the surface area for filtration within a compact design. The pleats allow for a large amount of filter material to be packed into a relatively small space. A baghouse filter, on the other hand, is shaped like a long bag or sock, typically made of woven or felted fabric. The dust-laden air enters from the top and passes through the bag's walls, leaving dust on the outside or inside of the bag, depending on the design. Each filter type is used for a specific type of dust collector.
Care and Maintenance of Dust Collector Cartridge Filters
Care and Maintenance of Dust Collector Cartridge Filters
How Often Should Cartridge Filters Be Replaced?
The frequency of cartridge filter replacement in a dust collection system can vary widely based on several factors, such as the type of particulates being filtered, the volume of dust, the quality of the filter, and the specific application and environment. As a rule of thumb, industrial cartridge air filters should be changed at least annually, though in some environments they may need to be replaced more often. Generally, a cartridge filter should be replaced when it shows signs of wear, damage, or reduced performance, which might be indicated by an increase in pressure drop across the filter, visible dust emission, or decreased airflow through the system. Regular inspection and adherence to a manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedule are crucial in determining the optimal replacement interval. Read more: How Often Should You Change Dust Collector Filters?
Learn more: Extending the Life of Cartridge Air Filters
What Are the Signs that a Cartridge Filter Needs to be Replaced?
Recognizing the signs that a cartridge filter needs replacement is vital in maintaining the effectiveness of a dust collection system. Common indicators include:
- Increased Pressure Drop: A notable increase in pressure drop across the filter may suggest that the filter is becoming clogged with particulates.
- Decreased Airflow: Reduced airflow through the dust collector is often a sign of filter obstructions or damage.
- Visible Emissions: Dust or particles being emitted from the system may indicate filter failure or inefficiency.
- Physical Damage: Any visible damage, such as tears, holes, or excessive wear on the filter material, warrants immediate replacement.
Proactively attending to filter replacement at the first sign of these issues will safeguard the system’s performance and maintain the quality of the filtered air. Always follow safety protocols and manufacturer guidelines when inspecting and replacing filters.
What Does Pressure Drop Mean for Cartridge Air Filters?
Pressure drop is defined as the difference in pressure between two points in a system, often measured at the inlet and outlet of a filter. It represents the resistance or loss encountered by the fluid (which can be air, water, or other liquids) as it flows through the filter media. In the context of cartridge filters, "pressure drop" refers to the reduction in air or fluid pressure as it passes through the filter cartridge. Essentially, it's a measure of the resistance that the filter introduces to the flow. The higher the resistance, the more energy it takes to move air through the system; a high filter drop makes the system work harder and use more energy to push air through the filters.
Pressure drop is often used as an indicator of filter loading; as filters become clogged with particulates, increased pressure drop will be noted across the filter. Other aspects that influence pressure drop include:
- Filtration efficiency: Filters with a higher MERV rating, or a HEPA rating, will have a larger pressure drop across the filter and require more energy to push air through.
- Media Type: Different filter media (e.g., pleated, spun, melt-blown) offer varying levels of resistance.
- Filter Design: The design of the cartridge, including the size, shape, pleat design, and density of the filter media, can influence pressure drop.
- Flow Rate: A higher flow rate can result in a higher pressure drop because more air is trying to pass through the filter in a given time.
Why Do I Need a Filter Pulsing Mechanism for Cartridge Air Filters?
A filter pulsing mechanism is crucial for cartridge air filters to effectively manage accumulated dust and sustain optimal filtration performance. The pulsing mechanism periodically releases short bursts of compressed air through the filter, dislodging collected particulates and maintaining a clear path for air to flow through the filter media. This process is crucial to prevent the excessive buildup of dust, which could otherwise hinder the filter’s performance, elevate pressure drops, and potentially lead to premature filter failure. Regularly pulsing the filter ensures that it continues to operate efficiently, maintains a consistent airflow, and prolongs the overall lifespan of the cartridge, thereby optimizing the functionality and cost-effectiveness of the dust collection system.
Are Cartridge Filters Washable?
The washability of cartridge filters largely depends on the filter’s material and construction. Some cartridge filters are designed to be washable and reusable (usually for a limited number of times). Washable cartridge filters are typically made of materials that can withstand the cleaning process without degrading, such as polyester, polypropylene, or nylon. On the other hand, many cartridge filters, especially those made of paper or other non-washable materials, are designed for single use and cannot be effectively cleaned through washing. It is essential to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to determine whether a specific cartridge filter is washable. Even for washable types, it’s crucial to follow recommended washing procedures to avoid damaging the filter and to ensure it maintains its filtration efficiency post-washing.
How Are Dust Collector Cartridge Filters Disposed Of?
Disposing of cartridge filters involves adhering to safety protocols, such as using appropriate personal protective equipment to manage potential exposure to collected particulates. Disposal protocols for used cartridge filters are highly dependent on the materials being filtered and their overall toxicity. Cartridge filters loaded with particulate considered hazardous to human health or the environment might require decontamination, special containment (e.g., Bag In/Bag Out or BIBO processes), or even professional hazardous waste management to ensure safe and compliant disposal. Filters used for less hazardous materials can often be disposed of via standard waste channels, always following local and industry-specific regulations. Some types of filter media may even be recyclable if the cartridges have not been used for hazardous material collection. Maintaining thorough documentation of filter disposal may be required for regulatory compliance, particularly when dealing with hazardous materials. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and local regulations to ensure appropriate disposal practices.
How Can I Extend the Life of Dust Collector Cartridge Filters?
Proper filter selection and maintenance will extend the life of cartridge dust collector filters. That starts with purchasing high-quality cartridge air filters with the right media type and filtration efficiency rating for the application. The dust collector should also have a filter pulsing mechanism to pulse excess dust off the filters. Ensuring that the dust collector system operates within the manufacturer’s specified parameters, such as maintaining appropriate air-to-cloth ratios and observing correct differential pressures, helps to prevent undue stress on the filters. For heavy or abrasive dust, protecting the filters using baffles, dropout boxes, or pre-filtration can also reduce wear and tear on filter media.
Learn more: Extending the Life of Cartridge Air Filters
Types of Cartridge Air Filters
Types of Cartridge Air Filters
What Are Dust Collector Cartridge Filters Made Of?
There are several types of filter media used for dust collector cartridges. Some of the most common types of dust collector cartridge filters include cellulose, spunbond polyesters, and cellulose-polyester blends.
- Cellulose cartridge filters are economical and typically have a MERV rating of 10-12. They are typically used for dry dust in standard applications.
- Spunbond polyester and cellulose-polyester blends are more durable and suitable for more challenging applications, such as high humidity/temperature or chemical exposure.
- Some cartridge filters have a layer of nanofiber over a foundational material such as polyester. Nanofiber has a high filtration efficiency for very fine or submicron particulate.
- Some air filter cartridges have specialized coatings, such as PTFE, for enhanced filtration efficiency and dust release. PTFE-coated filters are often recommended for moist, oily or sticky dust or challenging environments. (Note that dust that contains high levels of moisture or oil may require different dust collection methods, such as wet collection or an oil mist collector.)
What Is a Nano Cartridge Filter?
A nano cartridge filter refers to a filter that utilizes nanotechnology, typically featuring a nanofiber filtration media, to enhance particle capture efficiency and air permeability. The nanofiber media is composed of extremely fine fibers, often less than one micron in diameter, allowing it to trap sub-micron particles effectively while maintaining lower pressure drop compared to traditional media. This technology is particularly useful in applications that require high-efficiency filtration, such as in environments with fine, toxic, or otherwise challenging-to-capture particles. Nano cartridge filters often offer superior filtration performance, especially in capturing airborne particles, fumes, and smoke, while also often allowing for extended filter life and reduced energy consumption due to the lower resistance to airflow.
What Are PTFE-Coated Cartridge Filters Used For?
PTFE-coated cartridge filters are utilized in applications demanding high-efficiency filtration while navigating challenging environmental conditions. The polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coating enhances the filter’s resistance to moisture, chemicals, and oils, safeguarding the filter media and promoting longevity. The PTFE coating also promotes effective release of dust during filter pulsing for longer filter life, especially when collecting wet, hygroscopic, oily or sticky dust. Particularly prominent in industries dealing with fine, toxic, or oily dusts, these filters ensure optimal particulate capture and are advantageous where air quality and cross-contamination are critical concerns. PTFE-coated filters often provide lower pressure drop and thus can also contribute to energy savings within dust collection systems. Their robustness and enhanced filtration characteristics make them suitable for various industrial applications, including pharmaceutical, food processing, and manufacturing environments with moist or oily particulates.
What Are Antistatic Cartridge Filters?
Antistatic filters are designed to mitigate the buildup of static electricity within the filter media. They are predominantly used in environments where the presence of static electricity poses risks, such as in explosive or flammable atmospheres or for collection of static-containing or combustible dusts. The materials used in antistatic filters are either intrinsically conductive or are treated with an antistatic agent, facilitating the dissipation of electrical charges and thereby reducing the risk of spark generation. Industries like woodworking, grain processing, and any application involving combustible dust often utilize antistatic filters to adhere to safety regulations and to protect against the dangers of dust explosions or fires.
Applications
Applications
What Is the Best Dust Collector Cartridge Filter for Welding?
For welding fume collection, the best type of cartridge filter is one that provides effective filtration of fine, potentially toxic fumes and larger particles generated during welding processes. Often, filters with a nanofiber or PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) coating are preferred due to their capability to efficiently capture sub-micron particles while maintaining a lower pressure drop, ensuring energy-efficient operation. Filters should have a MERV rating of 15 or above for welding and other thermal applications producing submicron fumes. Fire-retardant properties and resistance to oil and moisture may also be needed to manage the various particulates and fumes found in welding environments. Additionally, compliance with relevant safety and air quality standards, such as those outlined by OSHA or other regulatory bodies, should guide the selection of a cartridge filter for welding applications, ensuring the safeguarding of both air quality and occupational health.
What Is the Best Cartridge Filter for Metal Cutting and Grinding?
Selecting the best cartridge filter for metal cutting and grinding dust involves considering the specific challenges posed by metal particulates, which can be fine, potentially toxic, and abrasive. For high volumes of fine grinding and cutting dust (such as dust produced by laser cutting or CNC machines), a filter with a nanofiber media or PTFE membrane may be recommended, as they can efficiently capture fine metal particles while maintaining a lower pressure drop and facilitate effective cleaning. Manual cutting and grinding tend to produce lower dust volumes and larger dust particles, so a standard MERV 11 cartridge filter may be adequate. The durability of the filter is crucial to managing the abrasive nature of metal dust, so a substrate made from robust, wear-resistant materials like spunbond polyester would be beneficial. If the metal dust is considered hazardous, as in the case of certain types of stainless steel, beryllium, or aluminum, a HEPA after-filter may be needed to ensure worker safety and compliance with PELs. Moreover, fire and explosion risks associated with certain metal dusts must be addressed, necessitating the inclusion of appropriate safety systems and potentially antistatic filter materials.
What Is the Best Dust Collector Cartridge Filter for Powder & Bulk Applications?
The best cartridge filter for powder and bulk applications should address the specific challenges posed by fine powder particles while handling varied particulate sizes and loadings effectively. A cartridge filter with a nanofiber layer or a PTFE membrane is often selected due to its ability to efficiently capture fine powders while maintaining a lower pressure drop, which translates to energy-efficient operation. The nanofiber or PTFE surface enables effective surface filtration, facilitates easier and more effective pulse cleaning and contributes to a longer filter life. Additionally, the filter’s physical attributes should be robust enough to manage the bulk materials, possibly incorporating abrasion-resistant features if the powders are abrasive. Paying attention to the particular characteristics of the powder (like combustibility. Particle size, abrasiveness, moisture levels and toxicity) and ensuring the chosen cartridge filter and dust collection system adhere to relevant safety and operational guidelines will contribute to effectively managing powder and bulk applications while maintaining a safe and compliant operation.
What Is the Best Air Cartridge Filter for Wet, Oily or Sticky Dust?
The best cartridge filter for handling moist, oily or sticky dust is typically one that features a moisture-resistant and non-stick surface, such as a PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) membrane, to effectively manage moisture-laden or adhesive particulates. PTFE-coated filters allow moist or sticky particulates to be more easily released during the filter pulsing process, minimizing potential clogging and promoting consistent airflow. Additionally, their hydrophobic nature prevents moisture absorption, which is critical in maintaining filter integrity and avoiding microbial growth in humid environments. (Note that dust that contains high levels of moisture or oil may require different dust collection methods, such as wet collection or an oil mist collector.) Ensuring the selected cartridge filter can proficiently handle the specific challenges posed by or sticky dust ensures sustained filtration performance and longevity in such demanding applications. In some cases, a washable filter media may be preferred.
What Is the Best Cartridge Filter for Abrasive Dust?
Applications such as seed processing, mining and mineral ore processing, and abrasive blasting tend to produce high levels of coarse, abrasive dust that can be tough on filters. For handling abrasive dust, the best cartridge filter should prioritize durability and robustness to withstand the wear and tear imposed by the harsh particulates. A cartridge filter with a substrate constructed from abrasion-resistant materials, such as spunbond polyester, can be advantageous due to its resilience against abrasive damage. A PTFE membrane or other specialized coatings may be recommended to increase filter performance and durability. It is also important to consider overall dust collection system design, including incorporation of filter-protecting elements such as dropout boxes, baffle systems or pre-filtration to optimize filter longevity and performance for abrasive dust applications.
What Is the Best Cartridge Air Filter for Combustible Dust?
The best cartridge filter for combustible dust must prioritize safety and compliance with regulatory standards to prevent ignition and contain potential deflagrations. Filters designed with antistatic or conductive materials, which mitigate the risk of spark generation from accumulated dust or during the cleaning cycle, are often recommended when handling combustible dusts, especially if static-based self-ignition is a concern. Moreover, using cartridge filters with efficient particulate release, such as those with a PTFE membrane, can help to keep dust from accumulating to hazardous levels inside the filter chamber. Integrating these specialized filters into a comprehensive, safety-focused dust collection system that includes features like explosion venting, isolation, and suppression systems in adherence with National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards will further safeguard against the risks posed by combustible dust in various industrial applications. Always consult with a qualified engineer or a dust safety specialist when dealing with combustible dust to ensure total system safety.
What Is the Best Cartridge Air Filter for Plastic Fines?
For managing plastic fines, you’ll want a cartridge filter that effectively captures these fine, lightweight particulates while maintaining efficient airflow. Filters with nanofiber media or those coated with a PTFE membrane are commonly utilized due to their adeptness at trapping fine particles without becoming prematurely clogged. The nanofiber media provides a surface layer of fine fibers that trap smaller particles, protecting the substrate below, while PTFE coatings allow for easier pulse cleaning due to their non-stick surface characteristics. Antistatic filter media may be needed when dealing with static-producing plastic fines. It’s also vital to ensure that the dust collector system is optimized for dealing with lightweight, floatable dust, which might involve considering factors like air-to-cloth ratio, filter cleaning mechanisms, and placement within the system to effectively manage plastic fines without losing filtration efficacy or overburdening the filter.
What Is the Best Dust Collector Cartridge Filter for Carbon Black?
Handling carbon black, which is known for its fine particulate size and potential health risks, necessitates a cartridge filter capable of capturing sub-micron particles while preventing exposure to workers and contamination in the workplace. Filters featuring a PTFE membrane or nanofiber media are commonly chosen for such applications due to their excellent fine particle capture efficiency. PTFE membranes can offer a smooth, non-stick surface, facilitating easier cleaning and ensuring longevity, while nanofiber media creates a barrier that prevents the penetration of tiny carbon black particles into the filter substrate. Additionally, selecting filters with a high MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) rating of 15 or 16, indicating superior fine particle filtration, alongside ensuring a well-designed dust collection system, will optimize the management of carbon black in a safe and efficient manner. Compliance with relevant occupational safety and air quality standards, including adherence to National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards for handling combustible dust, is also paramount in selecting and implementing filtration solutions for carbon black applications.





