Exposure Risks for Silica Dust
Exposure Risks for Silica Dust
Silica dust is inhaled into the lungs, where it is implicated in lung cancer as well as chronic bronchitis and other respiratory diseases. As the substance makes its way from the lungs through the body, silica can also damage other bodily systems, most notably the kidneys.
Exposure can also lead to a serious disease caused by damage to the lining of the lung sacs. Acute silicosis, caused by severe exposure, can cause the lungs to become inflamed and fill with fluid, creating a medical emergency. Chronic silicosis develops with even low-level exposure over time, reducing lung capacity until sufferers need oxygen to survive.
Because of the severity of silica dangers, manufacturers can't settle for filtering out 80% or so of the dust, as they might when working with wood dust or other non-carcinogenic materials. With silica, a manufacturer needs to aim for removing 99.9% of the dust.
 Regulations for Silica Dust
Regulations for Silica Dust
OSHA is the primary agency tasked with regulating silica dust. The administration recently made waves when it announced it was cutting permissible exposure levels (PELs) by half. You can find the final ruling here, but these are the basic facts: the PELs for crystalline silica have been lowered to 50 micrograms per cubic meter of air (μ/cu.m) as an 8-hour time-weighted average, down from the currently allowable 100 μ/cu.m TWA. The new rule takes effect June 23, 2016, and employers have until June 2018 to comply. The rule also outlines requirements for assessing and monitoring exposure, protecting employees, mitigation, record keeping and employee communication.
OSHA has made this rule change because scientific evidence shows that the previous exposure limits were not keeping workers safe. OSHA estimates that the new rule could prevent 600 deaths and 900 new cases of silicosis each year.
The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) recommends a lower exposure limit for silica: 25 micrograms per cubic meter. This lower limit is not a surprise, since ACGIH guidelines are usually more strict than OSHA standards. Many leading manufacturers, however, strive to meet ACGIH guidelines.
As with other OSHA regulations, failure to comply can bring serious fines. The administration can assess fines up to hundreds of thousands of dollars every time an offender is cited.
MORE DUST TYPES
Solutions for Silica Dust
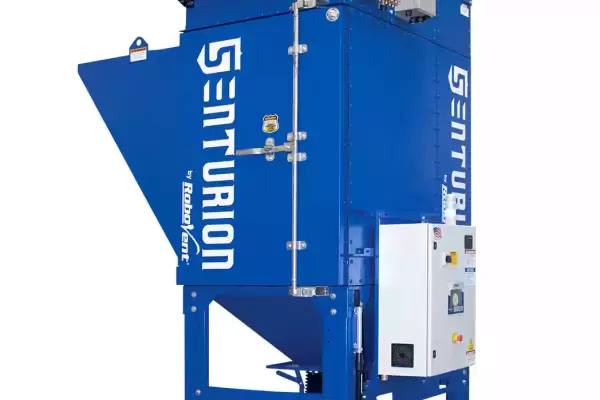
A variety of equipment exists to eliminate silica dust. These dust collectors will help businesses comply with OSHA's more stringent rules issued in 2016. Whether a business needs a source capture solution, an ambient capture one, or a combination of the two, RoboVent offers a wide variety of dust collectors and engineering services to meet any challenge.
Silica Dust Collection Systems Collectors
Clean Air Technology Services
CONTACT US
Contact one of our industrial dust experts to gain the advantage against dust-generating processes and applications.